 Home
Home
 Back
Back
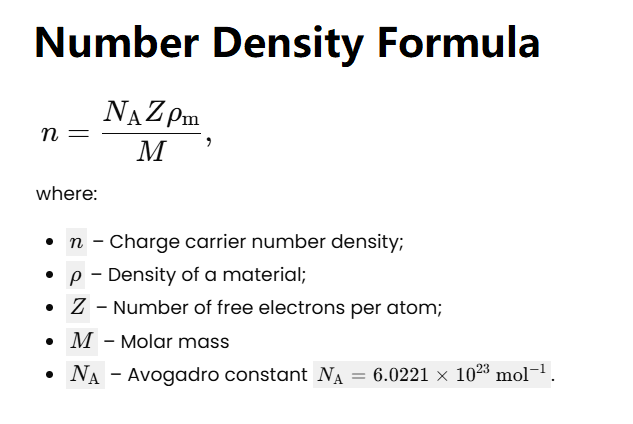
Number density refers to the number of particles (in this case, free electrons) per unit volume in a material, typically measured in electrons per cubic meter (m³) or cubic centimeter (cm³). For metals, the number density of free electrons is crucial for understanding electrical conductivity. It depends on the material’s density, molar mass, and the number of free electrons per atom, which varies depending on the material’s atomic structure.
This calculator allows you to compute the number density of free electrons by selecting a material or entering custom values for density and molar mass, along with the number of free electrons per atom.
Number Density Calculation: The number density of free electrons is calculated using the formula:
\(n = \frac{\rho \cdot N_A \cdot z}{M}\)
Where:
Example Calculation: Let’s calculate the number density for copper (\(\rho = 8960 \, \text{kg/m³}\), \(M = 63.55 \, \text{g/mol} = 0.06355 \, \text{kg/mol}\)) with 1 free electron per atom:
Use the form above to select a material or input custom values, along with the number of free electrons, to compute the number density.
The calculator includes the following materials with their respective densities and molar masses:
| Material | Density (kg/m³) | Molar Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 2700 | 26.98 |
| Copper | 8960 | 63.55 |
| Gold | 19300 | 196.97 |
| Silver | 10500 | 107.87 |
| Magnesium | 1740 | 24.31 |
| Tungsten | 19300 | 183.84 |
| Mercury | 13550 | 200.59 |
| Nickel | 8900 | 58.69 |
| Platinum | 21450 | 195.08 |
| Iron | 7870 | 55.85 |
Select "Custom" to input your own density and molar mass values.
The number of free electrons per atom (\(z\)) depends on the material’s atomic structure. For metals, this is typically the number of valence electrons that contribute to electrical conduction. Common values include:
Input the appropriate value for your material to calculate the number density.
How do you calculate number density?
To calculate the number density of free electrons:
What is the number density of copper with 1 free electron per atom?
For copper (\(\rho = 8960 \, \text{kg/m³}\), \(M = 63.55 \, \text{g/mol} = 0.06355 \, \text{kg/mol}\), \(z = 1\)):
\( n = \frac{8960 \cdot (6.022 \times 10^{23}) \cdot 1}{0.06355} \approx 8.486 \times 10^{28} \, \text{electrons/m³} \).